FFmpeg 开发
nginx+RTMP安装配置
| |
gstreamer安装
| |
ffmpeg安装
| |
gstreamer使用
摄像头视频流格式
| |
rtmp推流(失真和延时十分严重)
| |
FFmpeg参数参考
FFplay参数表
| 名称 | 有参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| x | Y | 强制屏幕宽度 |
| y | Y | 强制屏幕高度 |
| s | Y | 强制屏幕大小 |
| fs | N | 全屏 |
| an | N | 关闭音频 |
| vn | N | 关闭视频 |
| ast | Y | 设置想播放的音频流(需要指定流ID) |
| vst | Y | 设置想播放的视频流(需要指定流ID) |
| sst | Y | 设置想播放的字幕流(需要指定流ID) |
| ss | Y | 从指定位置开始播放,单位是秒 |
| t | Y | 播放指定时长的视频 |
| nodisp | N | 无显示屏幕 |
| f | Y | 强制封装格式 |
| pix_fmt | Y | 指定像素格式 |
| stats | N | 显示统计信息 |
| idct | Y | IDCT算法 |
| ec | Y | 错误隐藏方法 |
| sync | Y | 视音频同步方式(type=audio/video/ext) |
| autoexit | N | 播放完成自动退出 |
| exitonkeydown | N | 按下按键退出 |
| exitonmousedown | N | 按下鼠标退出 |
| loop | Y | 指定循环次数 |
| framedrop | N | CPU不够的时候丢帧 |
| window_title | Y | 显示窗口的标题 |
| rdftspeed | Y | Rdft速度 |
| showmode | Y | 显示方式(0 = video, 1 = waves, 2 = RDFT) |
| codec | Y | 强制解码器 |
FFplay播放时的快捷键
播放视音频文件的时候,可以通过下列按键控制视音频的播放
| 按键 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| q, ESC | 退出 |
| f | 全屏 |
| p, 空格 | 暂停 |
| w | 显示音频波形 |
| s | 逐帧显示 |
| 左方向键/右方向键 | 向后10s/向前10s |
| 上方向键/下方向键 | 向后1min/向前1min |
| page down/page up | 向后10min/向前10min |
| 鼠标点击屏幕 | 跳转到指定位置(根据鼠标位置相对屏幕的宽度计算) |
FFmpeg参数详解
a) 通用选项
| 参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -L | 许可证 |
| -h | 帮助 |
| -fromats | 显示可用的格式 |
| -f fmt | 强迫采用格式fmt |
| -i filename | 输入文件 |
| -y | 覆盖输出文件 |
| -t duration | 设置纪录时间 hh:mm:ss[.xxx]格式的记录时间也支持 |
| -ss position | 搜索到指定的时间 [-]hh:mm:ss[.xxx]的格式也支持 |
| -title string | 设置标题 |
| -author string | 设置作者 |
| -copyright string | 设置版权 |
| -comment string | 设置评论 |
| -target type | 设置目标文件类型(vcd,svcd,dvd) 所有的格式选项(比特率,编解码以及缓冲区大小)自动设置,只需要输入如下的就可以了:ffmpeg -i myfile.avi -target vcd /tmp/vcd.mpg |
| -hq | 激活高质量设置 |
| -itsoffset offset | 设置以秒为基准的时间偏移,该选项影响所有后面的输入文件。该偏移被加到输入文件的时戳,定义一个正偏移意味着相应的流被延迟了 offset秒。 [-]hh:mm:ss[.xxx]的格式也支持 |
b) 视频选项
-b bitrate 设置比特率,缺省200kb/s -r fps 设置帧频 缺省25 -s size 设置帧大小 格式为WXH 缺省160X128.下面的简写也可以直接使用: Sqcif 128X96 qcif 176X144 cif 252X288 4cif 704X576 -aspect aspect 设置横纵比 4:3 16:9 或 1.3333 1.7777 -croptop size 设置顶部切除带大小 像素单位 -cropbottom size –cropleft size –cropright size -padtop size 设置顶部补齐的大小 像素单位 -padbottom size –padleft size –padright size –padcolor color 设置补齐条颜色(hex,6个16进制的数,红:绿:兰排列,比如 000000代表黑色) -vn 不做视频记录 -bt tolerance 设置视频码率容忍度kbit/s -maxrate bitrate设置最大视频码率容忍度 -minrate bitreate 设置最小视频码率容忍度 -bufsize size 设置码率控制缓冲区大小 -vcodec codec 强制使用codec编解码方式。如果用copy表示原始编解码数据必须被拷贝。 -sameq 使用同样视频质量作为源(VBR) -pass n 选择处理遍数(1或者2)。两遍编码非常有用。第一遍生成统计信息,第二遍生成精确的请求的码率 -passlogfile file 选择两遍的纪录文件名为file
c)高级视频选项
-g gop_size 设置图像组大小 -intra 仅适用帧内编码 -qscale q 使用固定的视频量化标度(VBR) -qmin q 最小视频量化标度(VBR) -qmax q 最大视频量化标度(VBR) -qdiff q 量化标度间最大偏差 (VBR) -qblur blur 视频量化标度柔化(VBR) -qcomp compression 视频量化标度压缩(VBR) -rc_init_cplx complexity 一遍编码的初始复杂度 -b_qfactor factor 在p和b帧间的qp因子 -i_qfactor factor 在p和i帧间的qp因子 -b_qoffset offset 在p和b帧间的qp偏差 -i_qoffset offset 在p和i帧间的qp偏差 -rc_eq equation 设置码率控制方程 默认tex^qComp -rc_override override 特定间隔下的速率控制重载 -me method 设置运动估计的方法 可用方法有 zero phods log x1 epzs(缺省) full -dct_algo algo 设置dct的算法 可用的有 0 FF_DCT_AUTO 缺省的DCT 1 FF_DCT_FASTINT 2 FF_DCT_INT 3 FF_DCT_MMX 4 FF_DCT_MLIB 5 FF_DCT_ALTIVEC -idct_algo algo 设置idct算法。可用的有 0 FF_IDCT_AUTO 缺省的IDCT 1 FF_IDCT_INT 2 FF_IDCT_SIMPLE 3 FF_IDCT_SIMPLEMMX 4 FF_IDCT_LIBMPEG2MMX 5 FF_IDCT_PS2 6 FF_IDCT_MLIB 7 FF_IDCT_ARM 8 FF_IDCT_ALTIVEC 9 FF_IDCT_SH4 10 FF_IDCT_SIMPLEARM -er n 设置错误残留为n 1 FF_ER_CAREFULL 缺省 2 FF_ER_COMPLIANT 3 FF_ER_AGGRESSIVE 4 FF_ER_VERY_AGGRESSIVE -ec bit_mask 设置错误掩蔽为bit_mask,该值为如下值的位掩码 1 FF_EC_GUESS_MVS (default=enabled) 2 FF_EC_DEBLOCK (default=enabled) -bf frames 使用frames B 帧,支持mpeg1,mpeg2,mpeg4 -mbd mode 宏块决策 0 FF_MB_DECISION_SIMPLE 使用mb_cmp 1 FF_MB_DECISION_BITS 2 FF_MB_DECISION_RD -4mv 使用4个运动矢量 仅用于mpeg4 -part 使用数据划分 仅用于mpeg4 -bug param 绕过没有被自动监测到编码器的问题 -strict strictness 跟标准的严格性 -aic 使能高级帧内编码 h263+ -umv 使能无限运动矢量 h263+ -deinterlace 不采用交织方法 -interlace 强迫交织法编码仅对mpeg2和mpeg4有效。当你的输入是交织的并且你想要保持交织以最小图像损失的时候采用该选项。可选的方法是不交织,但是损失更大 -psnr 计算压缩帧的psnr -vstats 输出视频编码统计到vstats_hhmmss.log -vhook module 插入视频处理模块 module 包括了模块名和参数,用空格分开
D)音频选项
-ab bitrate 设置音频码率 -ar freq 设置音频采样率 -ac channels 设置通道 缺省为1 -an 不使能音频纪录 -acodec codec 使用codec编解码
E)音频/视频捕获选项
-vd device 设置视频捕获设备。比如/dev/video0 -vc channel 设置视频捕获通道 DV1394专用 -tvstd standard 设置电视标准 NTSC PAL(SECAM) -dv1394 设置DV1394捕获 -av device 设置音频设备 比如/dev/dsp
F)高级选项
-map file:stream 设置输入流映射 -debug 打印特定调试信息 -benchmark 为基准测试加入时间 -hex 倾倒每一个输入包 -bitexact 仅使用位精确算法 用于编解码测试 -ps size 设置包大小,以bits为单位 -re 以本地帧频读数据,主要用于模拟捕获设备 -loop 循环输入流(只工作于图像流,用于ffserver测试)
使用到的FFmpeg命令
查看视频信息
| |
- HEVC/H.265
- AVC/H.264
播放摄像头视频
| |
- -f:强制使用设定的格式解析
- video4linux2:(简称V4L2),是Linux中关于视频设备的内核驱动
- -framerate:指定帧率播放
- -video_size:设定播放视频尺寸
- hd720:720P分辨率
- /dev/video0:摄像头,在Linux里允许像读取文件一样读取摄像头数据
将本地摄像头数据用RTMP推流
| |
- -i:输入
- -f:强迫采用格式fmt
- flv:被众多新一代视频分享网站所采用,是增长最快、最为广泛的视频传播格式
保存RTSP流到本地文件
| |
- -vcodec copy:vcodec指定视频编码器,copy 指明只拷贝,不做编解码
- -acodec copy:acodec指定音频编码器,copy 指明只拷贝,不做编解码
播放RTSP流
| |
- -rtsp_transport tcp:ffmpeg默认采用UDP协议。当RTSP采用的是TCP协议时,直接播放就会报错,我们就需要指定协议
- -max_delay 5000000:指定最大延时为5000000微秒
RTSP流转RTMP流
| |
Unknown input format: ‘dshow’
| |
dshow是Windows DirectShow输入设备,linux无法使用
输出视频所有信息并以json形式展现
| |
音视频处理流程
FFmpeg主要结构体
结构体之间的关系
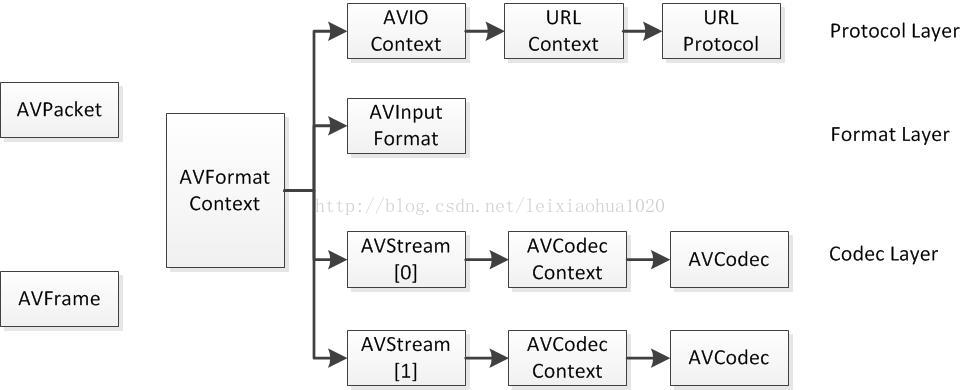
解协议
AVOutputFormat
主要功能:保存了输出格式(MP4、flv等)的信息和一些常规设置。
主要信息:
| |

AVFormatContext
主要功能:描述了一个媒体文件或媒体流的构成和基本信息
主要信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19struct AVInputFormat *iformat;//输入数据的封装格式。仅解封装用,由avformat_open_input()设置 struct AVOutputFormat *oformat;//输出数据的封装格式。仅封装用,调用者在avformat_write_header()之前设置 AVIOContext *pb; // I/O上下文 // 解封装:由用户在avformat_open_input()之前设置(然后用户必须手动关闭它)或通过avformat_open_input()设置 // 封装:由用户在avformat_write_header()之前设置。 调用者必须注意关闭/释放IO上下文 unsigned int nb_streams;//AVFormatContext.streams中元素的个数 AVStream **streams;//文件中所有流的列表 char filename[1024];//输入输出文件名 int64_t start_time;//第一帧的位置 int64_t duration;//流的持续时间 int64_t bit_rate;//总流比特率(bit / s),如果不可用则为0。 int64_t probesize;//从输入读取的用于确定输入容器格式的数据的最大大小。仅封装用,由调用者在avformat_open_input()之前设置。 AVDictionary *metadata;//元数据 AVCodec *video_codec;//视频编解码器 AVCodec *audio_codec;//音频编解码器 AVCodec *subtitle_codec;//字母编解码器 AVCodec *data_codec;//数据编解码器 int (*io_open)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext **pb, const char *url, int flags, AVDictionary **options);//打开IO stream的回调函数。 void (*io_close)(struct AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext *pb);//关闭使用AVFormatContext.io_open()打开的流的回调函数解封装
AVFormatContext
- 主要功能:
解码
AVStream
- 主要功能:存储每一个视频/音频流信息
- 主要信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27int index; //在AVFormatContext中的索引,这个数字是自动生成的,可以通过这个数字从AVFormatContext::streams表中索引到该流。 int id;//流的标识,依赖于具体的容器格式。解码:由libavformat设置。编码:由用户设置,如果未设置则由libavformat替换。 AVCodecContext *codec;//指向该流对应的AVCodecContext结构,调用avformat_open_input时生成。 AVRational time_base;//这是表示帧时间戳的基本时间单位(以秒为单位)。该流中媒体数据的pts和dts都将以这个时间基准为粒度。 int64_t start_time;//流的起始时间,以流的时间基准为单位。如需设置,100%确保你设置它的值真的是第一帧的pts。 int64_t duration;//解码:流的持续时间。如果源文件未指定持续时间,但指定了比特率,则将根据比特率和文件大小估计该值。 int64_t nb_frames; //此流中的帧数(如果已知)或0。 enum AVDiscard discard;//选择哪些数据包可以随意丢弃,不需要去demux。 AVRational sample_aspect_ratio;//样本长宽比(如果未知,则为0)。 AVDictionary *metadata;//元数据信息。 AVRational avg_frame_rate;//平均帧速率。解封装:可以在创建流时设置为libavformat,也可以在avformat_find_stream_info()中设置。封装:可以由调用者在avformat_write_header()之前设置。 AVPacket attached_pic;//附带的图片。比如说一些MP3,AAC音频文件附带的专辑封面。 int probe_packets;//编解码器用于probe的包的个数。 int codec_info_nb_frames;//在av_find_stream_info()期间已经解封装的帧数。 int request_probe;//流探测状态,1表示探测完成,0表示没有探测请求,rest 执行探测。 int skip_to_keyframe;//表示应丢弃直到下一个关键帧的所有内容。 int skip_samples;//在从下一个数据包解码的帧开始时要跳过的采样数。 int64_t start_skip_samples;//如果不是0,则应该从流的开始跳过的采样的数目。 int64_t first_discard_sample;//如果不是0,则应该从流中丢弃第一个音频样本。 int64_t pts_reorder_error[MAX_REORDER_DELAY+1]; uint8_t pts_reorder_error_count[MAX_REORDER_DELAY+1];//内部数据,从pts生成dts。 int64_t last_dts_for_order_check; uint8_t dts_ordered; uint8_t dts_misordered;//内部数据,用于分析dts和检测故障mpeg流。 AVRational display_aspect_ratio;//显示宽高比。AVCodecContext
- 主要功能:存储该视频/音频流使用解码方式的相关数据
- 主要信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17enum AVMediaType codec_type; //编解码器的类型(视频,音频...)。 const struct AVCodec *codec; //采用的解码器AVCodec(H.264,MPEG2...)。 int64_t bit_rate;//平均比特率。 uint8_t *extradata;//针对特定编码器包含的附加信息(例如对于H.264解码器来说,存储SPS,PPS等)。 int extradata_size; AVRational time_base;//时间的基准单位,根据该参数,可以把PTS转化为实际的时间(单位为秒s)。 编解码延迟。 int delay;//编码:从编码器输入到解码器输出的帧延迟数。解码:除了规范中规定的标准解码器外产生的帧延迟数。 int width, height;//代表宽和高(仅视频)。 int refs;//运动估计参考帧的个数(H.264的话会有多帧,MPEG2这类的一般就没有了)。 int sample_rate; //采样率(仅音频)。 int channels; //声道数(仅音频)。 enum AVSampleFormat sample_fmt; //音频采样格式,编码:由用户设置。解码:由libavcodec设置。 int frame_size;//音频帧中每个声道的采样数。编码:由libavcodec在avcodec_open2()中设置。 解码:可以由一些解码器设置以指示恒定的帧大小. int frame_number;//帧计数器,由libavcodec设置。解码:从解码器返回的帧的总数。编码:到目前为止传递给编码器的帧的总数。 uint64_t channel_layout;//音频声道布局。编码:由用户设置。解码:由用户设置,可能被libavcodec覆盖。 enum AVAudioServiceType audio_service_type;//音频流传输的服务类型。编码:由用户设置。解码:由libavcodec设置。AVCodec
- 主要功能:存储编解码器信息
- 主要信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15const char *name;//编解码器的名字,比较短。在编码器和解码器之间是全局唯一的。 这是用户查找编解码器的主要方式 const char *long_name;//编解码器的名字,全称,比较长 enum AVMediaType type;//指明了类型,是视频,音频,还是字幕 enum AVCodecID id; const AVRational *supported_framerates;//支持的帧率(仅视频) const enum AVPixelFormat *pix_fmts;//支持的像素格式(仅视频) const int *supported_samplerates;//支持的采样率(仅音频) const enum AVSampleFormat *sample_fmts;//支持的采样格式(仅音频) const uint64_t *channel_layouts;//支持的声道数(仅音频) int priv_data_size;//私有数据的大小 void (*init_static_data)(struct AVCodec *codec);//初始化编解码器静态数据,从avcodec_register()调用 int (*encode2)(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *avpkt, const AVFrame *frame, int *got_packet_ptr);//将数据编码到AVPacket int (*decode)(AVCodecContext *, void *outdata, int *outdata_size, AVPacket *avpkt);//解码数据到AVPacket int (*close)(AVCodecContext *);//关闭编解码器。 void (*flush)(AVCodecContext *);//刷新缓冲区。当seek时会被调用关系
graph TD A[AVStream] --> B[AVCodecContext] B --> C[AVCodec]存数据
AVPacket
- 主要功能:存储压缩编码数据相关信息,即解码前数据(例如H.264码流)
- 主要信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14int64_t pts;// 显示时间,结合AVStream->time_base转换成时间戳 int64_t dts;// 解码时间,结合AVStream->time_base转换成时间戳 int size;//data的大小 int stream_index;//packet在stream的index位置 int flags;//标示,结合AV_PKT_FLAG使用,其中最低为1表示该数据是一个关键帧。 #define AV_PKT_FLAG_KEY 0x0001 //关键帧 #define AV_PKT_FLAG_CORRUPT 0x0002 //损坏的数据 #define AV_PKT_FLAG_DISCARD 0x0004 //丢弃的数据 int side_data_elems;//边缘数据元数个数 int64_t duration;//数据的时长,以所属媒体流的时间基准为单位,未知则值为默认值0 int64_t pos;//数据在流媒体中的位置,未知则值为默认值-1 uint8_t *data;//指向保存压缩数据的指针,这就是AVPacket的实际数据。 AVPacketSideData *side_data;//容器提供的一些附加数据 AVBufferRef *buf;//用来管理data指针引用的数据缓存AVFrame
- 主要功能:解码后数据(YUV/RGB像素数据)。AVFrame必须由** av_frame_alloc()分配内存**,同时必须由av_frame_free()释放,分配内存后能够被多次用来存储不同的数据。
- 主要信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18uint8_t * data [AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];//解码后原始数据(对视频来说是YUV,RGB,对音频来说是PCM)。 int linesize[AV_NUM_DATA_POINTERS];//在视频中,表示图片一行数据的大小。 uint8_t **extended_data;//指向数据平面/通道。 int width, height;//一个视频帧的宽度和高度。 int nb_samples;//这个AVFrame中的每个音频通道中包含的音频帧个数。 int format;//表示解码后的数据类型或格式,-1表示未被设置或不能识别的类型。 int key_frame;//是否为关键帧。 enum AVPictureType pict_type;//帧的类型。 AVRational sample_aspect_ratio;//视频帧的宽高比,0表示未知。 int64_t pts;//显示时间戳,表示该什么时候被显示。 int64_t pkt_dts;//从AVPacket中拷贝的值。 int coded_picture_number;//编码帧序号。 int display_picture_number;//显示帧需要。 void *opaque;//用户私有信息。 int repeat_pict;//解码时,每帧图片延迟的时间,extra_delay = repeat_pict / (2*fps)。 int interlaced_frame;//是否是隔行扫描 int sample_rate;//音频的采样率。 uint64_t channel_layout;//音频的布局方式。常用函数
av_register_all()
功能:该函数在所有基于ffmpeg的应用程序中几乎都是第一个被调用的。只有调用了该函数,才能使用复用器,编码器等。
avformat_network_init()
功能:使用ffmpeg类库进行开发时,打开流媒体(或本地文件)的函数是 avformat_open_input();
其中打开网络流的话,需要在前面调用函数 avformat_network_init()。
avformat_open_input()
功能:打开多媒体数据并且获得一些相关的信息
| |
参数:
ps:函数调用成功之后处理过的AVFormatContext结构体;
url:打开的视音频流的URL;
fmt:强制指定AVFormatContext中AVInputFormat的。这个参数一般情况下可以设置为NULL,这样FFmpeg可以自动检测AVInputFormat;
options:附加的一些选项,一般情况下可以设置为NULL
返回值:
执行成功的话,其返回值大于等于0
avformat_find_stream_info()
功能:读取一部分视音频数据并且获得一些相关的信息
| |
参数:
ic:输入的AVFormatContext;
options:配置和定义播放器的参数
返回值:函数正常执行后返回值大于等于0
在一些格式当中没有头部信息(flv、h264),此时调用avformat_open_input()在打开文件无法获取到里面的信息。此时就可以调用此函数,该函数会尝试去探测文件的格式,如果格式当中没有头部信息,它只能获取到编码、宽高等信息,无法获得总时长。如果无法获取到总时长,则需要把整个文件读一遍,计算一下它的总帧数:
| |
av_dump_format()
功能:打印视频流的信息
| |
参数:
ic:要分析的上下文
index:要转储有关信息的流的索引
url:要打印的URL,例如源文件或目标文件
is_output:选择指定的上下文是输入(0)还是输出(1)
avformat_alloc_output_context2()
**功能:**初始化一个用于输出的AVFormatContext结构体
| |
参数:
ctx:函数调用成功之后创建的AVFormatContext结构体
oformat:指定AVFormatContext中的AVOutputFormat,用于确定输出格式。如果指定为NULL,可以设定后两个参数(format_name或者filename)由FFmpeg猜测输出格式PS:使用该参数需要自己手动获AVOutputFormat,相对于使用后两个参数来说要麻烦一些
format_name:指定输出格式的名称。根据格式名称,FFmpeg会推测输出格式。输出格式可以是“flv”,“mkv”等等
filename:指定输出文件的名称。根据文件名称,FFmpeg会推测输出格式。文件名称可以是“xx.flv”,“yy.mkv”等等
返回值:
函数执行成功的话,其返回值大于等于0
avformat_new_stream()
**功能:**在 AVFormatContext 里创建 AVStream 通道,即为文件添加音视频流
| |
参数:
s:视频流上下文
c:如果非空,则与新流对应的AVCodecContext将被初始化以使用此编解码器。因此如果编解码器已知,则应提供编解码器。
返回值:
正常执行则返回新创建的流,出错时返回空
avcodec_copy_context()
**功能:**拷贝输入视频码流的AVCodecContex的数值到输出视频的AVCodecContext
| |
参数:
dest:目标编解码器上下文
src:源编解码器上下文
返回值:
成功时返回0
新版本中FFmpeg的avcodec_copy_context被avcodec_parameters_to_context和avcodec_parameters_from_context所替代,因此需要将原本的写法修改一下:
旧版API:
| |
新版API:
| |
avio_open()
avio_open(),是FFmepeg早期版本。avio_open()比avio_open2()少了最后2个参数。而它前面几个参数的含义和avio_open2()是一样的。从源代码中可以看出,avio_open()内部调用了avio_open2(),并且把avio_open2()的后2个参数设置成了NULL,因此它的功能实际上和avio_open2()都是用于打开FFmpeg的输入输出文件的。其源码如下所示:
| |
avio_open2()
**功能:**打开FFmpeg的输入输出文件
| |
参数:
s:函数调用成功之后创建的AVIOContext结构体
url:输入输出协议的地址
flags:打开地址的方式。可以选择只读,只写,或者读写,取值如下
- AVIO_FLAG_READ:只读
- AVIO_FLAG_WRITE:只写
- AVIO_FLAG_READ_WRITE:读写
int_cb:在协议级使用的中断回调
options:设置
返回值:
成功时返回值大于等于0,出错时对应AVERROR代码
avformat_write_header()
avformat_write_header(),av_write_frame()以及av_write_trailer()这三个函数一般是配套使用,其中av_write_frame()用于写视频数据(,avformat_write_header()用于写视频文件头,而av_write_trailer()用于写视频文件尾
**功能:**写视频文件头
| |
参数:
s:用于输出的AVFormatContext
options:额外的选项,一般为NULL
返回值:
函数正常执行后返回值等于0
av_interleaved_write_frame()
**功能:**将数据包写入输出媒体文件,以确保正确的交织。
| |
参数:
s:用于输出的AVFormatContext
pkt:包含要写入的数据的包
返回值:
函数正常执行后返回值等于0
av_write_frame()
**功能:**输出一帧视音频数据
| |
参数:
s:用于输出的AVFormatContext
pkt:等待输出的AVPacket
返回值:
函数正常执行后返回值等于0
av_write_trailer()
**功能:**输出文件尾
| |
参数:
s:用于输出的AVFormatContext
返回值:
函数正常执行后返回值等于0
av_read_frame()
功能:读取码流中的音频若干帧或者视频一帧
| |
参数:
s:输入的AVFormatContext
pkt:输出的AVPacket
返回值:
成功返回0
av_free_packet()
功能:释放 packet 占用的资源
| |
参数:
packet:需要是释放的packet
新的API:
| |
avformat_close_input()
功能:关闭一个AVFormatContext,一般和 avformat_open_input() 成对出现
| |
avio_close()
**功能:**关闭AVIOContext访问的资源并释放(只能用于被 avio_open() 打开的)
| |
av_gettime()
**功能:**以微秒为单位获取当前时间。
由于int64_t最大为9,223,372,036,854,775,807,因此会发生溢出的情况,得到的时间戳有正有负
音视频基础知识
FFmpeg中的时间处理
I、P、B 帧
I 帧、P 帧、B 帧的区别在于:
- I 帧(Intra coded frames):I 帧图像采用帧内编码方式,即只利用了单帧图像内的空间相关性,而没有利用时间相关性。I 帧使用帧内压缩,不使用运动补偿,由于 I 帧不依赖其它帧,所以是随机存取的入点,同时是解码的基准帧。I 帧主要用于接收机的初始化和信道的获取,以及节目的切换和插入,I 帧图像的压缩倍数相对较低。I 帧图像是周期性出现在图像序列中的,出现频率可由编码器选择。
- P 帧(Predicted frames):P 帧和 B 帧图像采用帧间编码方式,即同时利用了空间和时间上的相关性。P 帧图像只采用前向时间预测,可以提高压缩效率和图像质量。P 帧图像中可以包含帧内编码的部分,即 P 帧中的每一个宏块可以是前向预测,也可以是帧内编码。
- B 帧(Bi-directional predicted frames):B 帧图像采用双向时间预测,可以大大提高压缩倍数。值得注意的是,由于 B 帧图像采用了未来帧作为参考,因此 MPEG-2 编码码流中图像帧的传输顺序和显示顺序是不同的。
也就是说,一个 I 帧可以不依赖其他帧就解码出一幅完整的图像,而 P 帧、B 帧不行。P 帧需要依赖视频流中排在它前面的帧才能解码出图像。B 帧则需要依赖视频流中排在它前面或后面的帧才能解码出图像。
这就带来一个问题:在视频流中,先到来的 B 帧无法立即解码,需要等待它依赖的后面的 I、P 帧先解码完成,这样一来播放时间与解码时间不一致了,顺序打乱了,那这些帧该如何播放呢?这时就需要我们来了解另外两个概念:DTS 和 PTS
DTS、PTS 的概念
DTS、PTS 的概念如下所述:
- DTS(Decoding Time Stamp):即解码时间戳,这个时间戳的意义在于告诉播放器该在什么时候解码这一帧的数据。
- PTS(Presentation Time Stamp):即显示时间戳,这个时间戳用来告诉播放器该在什么时候显示这一帧的数据。
需要注意的是:虽然 DTS、PTS 是用于指导播放端的行为,但它们是在编码的时候由编码器生成的。
当视频流中没有 B 帧时,通常 DTS 和 PTS 的顺序是一致的。但如果有 B 帧时,就回到了我们前面说的问题:解码顺序和播放顺序不一致了。
比如一个视频中,帧的显示顺序是:I B B P,现在我们需要在解码 B 帧时知道 P 帧中信息,因此这几帧在视频流中的顺序可能是:I P B B,这时候就体现出每帧都有 DTS 和 PTS 的作用了。DTS 告诉我们该按什么顺序解码这几帧图像,PTS 告诉我们该按什么顺序显示这几帧图像。顺序大概如下:
PTS: 1 4 2 3
DTS: 1 2 3 4
Stream: I P B B
AVRational
- 主要功能:表示时间刻度
- 主要信息:
| |
时间单位
AV_TIME_BASE
ffmpeg中的内部计时单位(时间基),ffmepg中的所有时间都是于它为一个单位,比如AVStream中的duration即以为着这个流的长度为duration个AV_TIME_BASE。AV_TIME_BASE定义为:
| |
AV_TIME_BASE_Q
ffmpeg内部时间基的分数表示,实际上它是AV_TIME_BASE的倒数。从它的定义能很清楚的看到这点:
| |
av_rescale_q(int64_t a, AVRational bq, AVRational cq)
功能:计算a*bq / cq来把时间戳从一个时间基调整到另外一个时间基。在进行时间基转换的时候,应该首先这个函数,因为它可以避免溢出的情况发生。
av_rescale_q_rnd(int64_t a, AVRational bq, AVRational cq, enum AVRounding rnd)
| |
功能:将以 “时钟基c” 表示的 数值a 转换成以 “时钟基b” 来表示。
| |
AV_ROUND_ZERO = 0, // Round toward zero. 趋近于0 AV_ROUND_INF = 1, // Round away from zero. 趋远于0 AV_ROUND_DOWN = 2, // Round toward -infinity. 趋于更小的整数 AV_ROUND_UP = 3, // Round toward +infinity. 趋于更大的整数 AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF = 5, // Round to nearest and halfway cases away from zero. 四舍五入,小于0.5取值趋向0,大于0.5取值趋远于0
av_q2d()
| |
**功能:**将AVRatioal结构转换成double
av_usleep()
| |
功能:发送流媒体的数据的时候需要延时。不然的话,FFmpeg处理数据速度很快,瞬间就能把所有的数据发送出去,流媒体服务器是接受不了的。因此需要按照视频实际的帧率发送数据。本文记录的推流器在视频帧与帧之间采用了av_usleep()函数休眠的方式来延迟发送。这样就可以按照视频的帧率发送数据了。
根据PTS计算一帧在整个视频中的位置
| |
计算视频长度的方法
| |
时间基转换公式
- timestamp(ffmpeg内部时间戳) = AV_TIME_BASE * time(秒)
- time(秒) = AV_TIME_BASE_Q * timestamp(ffmpeg内部时间戳)