阅读量:
Socks5 代理
SOCKS是一种网络传输协议,名字取自 SOCKetS,主要用于客户端与外网服务器之间通讯的中间传递。
Socks5 是 Socks 协议的第五个版本,在 Socks4 的基础上增加了 UDP 转发和认证功能。
Socks 的流程为:
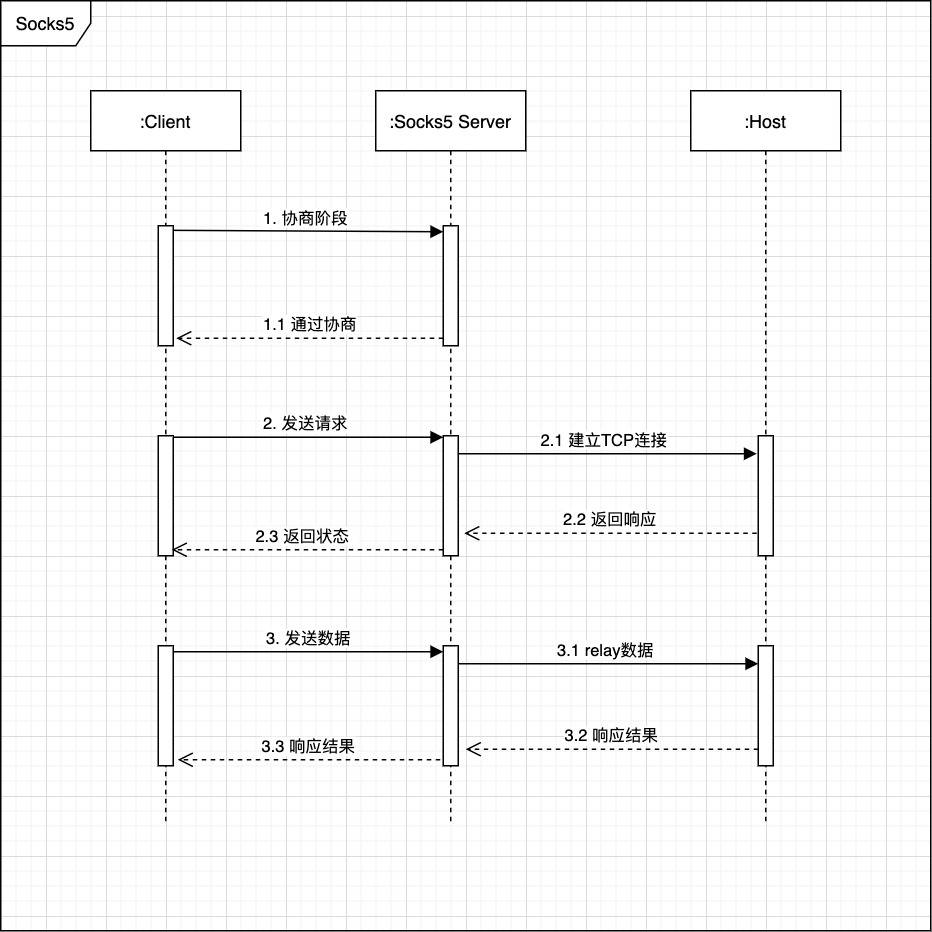
实现代码
package socks5
import (
"context"
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"io"
"net"
"strconv"
"time"
"github.com/gogf/gf/v2/os/glog"
)
// Authentication METHODs described in RFC 1928, section 3.
const (
noAuthRequired byte = 0
passwordAuth byte = 2
noAcceptableAuth byte = 255
)
// passwordAuthVersion is the auth version byte described in RFC 1929.
const passwordAuthVersion = 1
// socks5Version is the byte that represents the SOCKS version
// in requests.
const socks5Version byte = 5
// commandType are the bytes sent in SOCKS5 packets
// that represent the kind of connection the client needs.
type commandType byte
// The set of valid SOCKS5 commands as described in RFC 1928.
const (
connect commandType = 1
bind commandType = 2
udpAssociate commandType = 3
)
// addrType are the bytes sent in SOCKS5 packets
// that represent particular address types.
type addrType byte
// The set of valid SOCKS5 address types as defined in RFC 1928.
const (
ipv4 addrType = 1
domainName addrType = 3
ipv6 addrType = 4
)
// replyCode are the bytes sent in SOCKS5 packets
// that represent replies from the server to a client
// request.
type replyCode byte
// The set of valid SOCKS5 reply types as per the RFC 1928.
const (
success replyCode = 0
generalFailure replyCode = 1
connectionNotAllowed replyCode = 2
networkUnreachable replyCode = 3
hostUnreachable replyCode = 4
connectionRefused replyCode = 5
ttlExpired replyCode = 6
commandNotSupported replyCode = 7
addrTypeNotSupported replyCode = 8
)
// Server is a SOCKS5 proxy server.
type Server struct {
ctx context.Context
// Logf optionally specifies the logger to use.
// If nil, the standard logger is used.
Logf *glog.Logger
// Dialer optionally specifies the dialer to use for outgoing connections.
// If nil, the net package's standard dialer is used.
Dialer func(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error)
// Username and Password, if set, are the credential clients must provide.
Username string
Password string
}
func (s *Server) dial(ctx context.Context, network, addr string) (net.Conn, error) {
dial := s.Dialer
if dial == nil {
dialer := &net.Dialer{}
dial = dialer.DialContext
}
return dial(ctx, network, addr)
}
func (s *Server) logf(format string, args ...any) {
if s.Logf == nil {
s.Logf = glog.New()
s.Logf.SetFlags(glog.F_TIME_STD | glog.F_FILE_SHORT)
}
s.Logf.Infof(s.ctx, format, args...)
}
// Serve accepts and handles incoming connections on the given listener.
func (s *Server) Serve(l net.Listener) error {
defer l.Close()
for {
c, err := l.Accept()
if err != nil {
return err
}
go func() {
defer c.Close()
conn := &Conn{clientConn: c, srv: s}
err := conn.Run()
if err != nil {
s.logf("client connection failed: %v", err)
}
}()
}
}
// Conn is a SOCKS5 connection for client to reach
// server.
type Conn struct {
// The struct is filled by each of the internal
// methods in turn as the transaction progresses.
srv *Server
clientConn net.Conn
request *request
}
// Run starts the new connection.
func (c *Conn) Run() error {
needAuth := c.srv.Username != "" || c.srv.Password != ""
authMethod := noAuthRequired
if needAuth {
authMethod = passwordAuth
}
err := parseClientGreeting(c.clientConn, authMethod)
if err != nil {
c.clientConn.Write([]byte{socks5Version, noAcceptableAuth})
return err
}
c.clientConn.Write([]byte{socks5Version, authMethod})
if !needAuth {
return c.handleRequest()
}
user, pwd, err := parseClientAuth(c.clientConn)
if err != nil || user != c.srv.Username || pwd != c.srv.Password {
c.clientConn.Write([]byte{1, 1}) // auth error
return err
}
c.clientConn.Write([]byte{1, 0}) // auth success
return c.handleRequest()
}
func (c *Conn) handleRequest() error {
req, err := parseClientRequest(c.clientConn)
if err != nil {
res := &response{reply: generalFailure}
buf, _ := res.marshal()
c.clientConn.Write(buf)
return err
}
if req.command != connect {
res := &response{reply: commandNotSupported}
buf, _ := res.marshal()
c.clientConn.Write(buf)
return fmt.Errorf("unsupported command %v", req.command)
}
c.request = req
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
defer cancel()
srv, err := c.srv.dial(
ctx,
"tcp",
net.JoinHostPort(c.request.destination, strconv.Itoa(int(c.request.port))),
)
if err != nil {
res := &response{reply: generalFailure}
buf, _ := res.marshal()
c.clientConn.Write(buf)
return err
}
defer srv.Close()
serverAddr, serverPortStr, err := net.SplitHostPort(srv.LocalAddr().String())
if err != nil {
return err
}
serverPort, _ := strconv.Atoi(serverPortStr)
var bindAddrType addrType
if ip := net.ParseIP(serverAddr); ip != nil {
if ip.To4() != nil {
bindAddrType = ipv4
} else {
bindAddrType = ipv6
}
} else {
bindAddrType = domainName
}
res := &response{
reply: success,
bindAddrType: bindAddrType,
bindAddr: serverAddr,
bindPort: uint16(serverPort),
}
buf, err := res.marshal()
if err != nil {
res = &response{reply: generalFailure}
buf, _ = res.marshal()
}
c.clientConn.Write(buf)
errc := make(chan error, 2)
go func() {
_, err := io.Copy(c.clientConn, srv)
if err != nil {
err = fmt.Errorf("from backend to client: %w", err)
}
errc <- err
}()
go func() {
_, err := io.Copy(srv, c.clientConn)
if err != nil {
err = fmt.Errorf("from client to backend: %w", err)
}
errc <- err
}()
return <-errc
}
// parseClientGreeting parses a request initiation packet.
func parseClientGreeting(r io.Reader, authMethod byte) error {
var hdr [2]byte
_, err := io.ReadFull(r, hdr[:])
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("could not read packet header")
}
if hdr[0] != socks5Version {
return fmt.Errorf("incompatible SOCKS version")
}
count := int(hdr[1])
methods := make([]byte, count)
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, methods)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("could not read methods")
}
for _, m := range methods {
if m == authMethod {
return nil
}
}
return fmt.Errorf("no acceptable auth methods")
}
func parseClientAuth(r io.Reader) (usr, pwd string, err error) {
var hdr [2]byte
if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, hdr[:]); err != nil {
return "", "", fmt.Errorf("could not read auth packet header")
}
if hdr[0] != passwordAuthVersion {
return "", "", fmt.Errorf("bad SOCKS auth version")
}
usrLen := int(hdr[1])
usrBytes := make([]byte, usrLen)
if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, usrBytes); err != nil {
return "", "", fmt.Errorf("could not read auth packet username")
}
var hdrPwd [1]byte
if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, hdrPwd[:]); err != nil {
return "", "", fmt.Errorf("could not read auth packet password length")
}
pwdLen := int(hdrPwd[0])
pwdBytes := make([]byte, pwdLen)
if _, err := io.ReadFull(r, pwdBytes); err != nil {
return "", "", fmt.Errorf("could not read auth packet password")
}
return string(usrBytes), string(pwdBytes), nil
}
// request represents data contained within a SOCKS5
// connection request packet.
type request struct {
command commandType
destination string
port uint16
destAddrType addrType
}
// parseClientRequest converts raw packet bytes into a
// SOCKS5Request struct.
func parseClientRequest(r io.Reader) (*request, error) {
var hdr [4]byte
_, err := io.ReadFull(r, hdr[:])
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("could not read packet header")
}
cmd := hdr[1]
destAddrType := addrType(hdr[3])
var destination string
var port uint16
if destAddrType == ipv4 {
var ip [4]byte
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, ip[:])
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("could not read IPv4 address")
}
destination = net.IP(ip[:]).String()
} else if destAddrType == domainName {
var dstSizeByte [1]byte
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, dstSizeByte[:])
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("could not read domain name size")
}
dstSize := int(dstSizeByte[0])
domainName := make([]byte, dstSize)
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, domainName)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("could not read domain name")
}
destination = string(domainName)
} else if destAddrType == ipv6 {
var ip [16]byte
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, ip[:])
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("could not read IPv6 address")
}
destination = net.IP(ip[:]).String()
} else {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unsupported address type")
}
var portBytes [2]byte
_, err = io.ReadFull(r, portBytes[:])
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("could not read port")
}
port = binary.BigEndian.Uint16(portBytes[:])
return &request{
command: commandType(cmd),
destination: destination,
port: port,
destAddrType: destAddrType,
}, nil
}
// response contains the contents of
// a response packet sent from the proxy
// to the client.
type response struct {
reply replyCode
bindAddrType addrType
bindAddr string
bindPort uint16
}
// marshal converts a SOCKS5Response struct into
// a packet. If res.reply == Success, it may throw an error on
// receiving an invalid bind address. Otherwise, it will not throw.
func (res *response) marshal() ([]byte, error) {
pkt := make([]byte, 4)
pkt[0] = socks5Version
pkt[1] = byte(res.reply)
pkt[2] = 0 // null reserved byte
pkt[3] = byte(res.bindAddrType)
if res.reply != success {
return pkt, nil
}
var addr []byte
switch res.bindAddrType {
case ipv4:
addr = net.ParseIP(res.bindAddr).To4()
if addr == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid IPv4 address for binding")
}
case domainName:
if len(res.bindAddr) > 255 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid domain name for binding")
}
addr = make([]byte, 0, len(res.bindAddr)+1)
addr = append(addr, byte(len(res.bindAddr)))
addr = append(addr, []byte(res.bindAddr)...)
case ipv6:
addr = net.ParseIP(res.bindAddr).To16()
if addr == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid IPv6 address for binding")
}
default:
return nil, fmt.Errorf("unsupported address type")
}
pkt = append(pkt, addr...)
pkt = binary.BigEndian.AppendUint16(pkt, uint16(res.bindPort))
return pkt, nil
}