阅读量:
电影评论分类:二分类问题
简介
本例出自《Python 深度学习》,自己做了一个简单的总结归纳。
完整代码请参考:https://github.com/fchollet/deep-learning-with-python-notebooks
主要流程
数据预处理
graph LR
A[原始评论] --> |关键词分割|C[建立关键词索引]
C --> |将关键词转索引|D[原始评论转向量]
D --> 列表编码为二进制矩阵graph LR
原始评论标签 --> 二制化标签训练模型
graph LR
A1(第一层:16个输出单元) --> A[构建模型]
A2(第二层:16个输出单元) --> A
A3(第三层:1个输出单元) --> A
A ==> B[编译模型]
B1(配置优化器和损失函数) --> B
B ==> C[加入验证集训练模型]
C ==> D[绘制图表观察模型最佳参数]
D1[欠拟合与过拟合之间] --> D
D ==> E[选择最佳参数训练模型]
E ==> F[在新数据上使用模型]代码
加载数据集
注意:第一次加载会下载文件,速度较慢
from keras.datasets import imdb
# 加载 IMDB 数据集
(train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels) = imdb.load_data(num_words=10000) # 取一万个词
整数序列转二进制矩阵
import numpy as np
# 将整数序列编码为二进制矩阵
def vectorize_sequences(sequences, dimension=10000):
print((len(sequences), dimension))
results = np.zeros((len(sequences), dimension))
for i, sequence in enumerate(sequences):
results[i, sequence] = 1.
return results
x_train = vectorize_sequences(train_data)
x_test = vectorize_sequences(test_data)
向量标签化
# 标签向量化
y_train = np.asarray(train_labels).astype('float32') # int64转float32
y_test = np.asarray(test_labels).astype('float32')
构建模型
# 构建网络
from keras import layers
from keras import models
model = models.Sequential()
# 第一层,16个隐藏单元,激活函数为relu
model.add(layers.Dense(16, activation='relu', input_shape=(10000, )))
# 第二层,16个隐藏单元,激活函数为relu
model.add((layers.Dense(16, activation='relu')))
# 第三层,输出一个标量(预测结果),激活函数为sigmoid
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
编译模型
# 编译模型
# 优化器:rmsprop
# 损失函数:binary_crossentropy(仅包含一个单元的模型可以采用,替代方案:mean_squared_error)
# 指标:精确
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
加入验证集训练模型
# 留出验证集
x_val = x_train[:10000]
partial_x_train = x_train[10000:]
y_val = y_train[:10000]
partial_y_train = y_train[10000:]
# 训练模型
history = model.fit(partial_x_train, partial_y_train, epochs=20, batch_size=512, validation_data=(x_val, y_val))
绘制图表观察训练过程
history_dict = history.history
# 绘制训练损失和验证损失
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
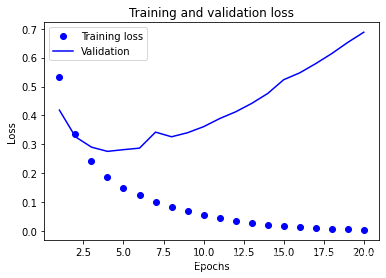
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# 绘制训练精度和验证精度
plt.clf() # 清空图像
acc = history.history['accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_accuracy']
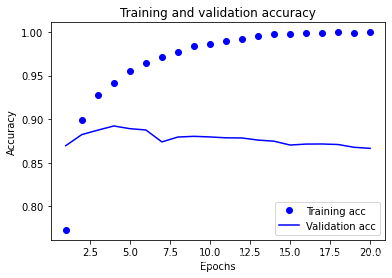
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
训练模型
对新数据进行预测
绘制图表
训练损失和验证损失
# 绘制训练损失和验证损失
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(loss) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
训练精度和验证精度
# 绘制训练精度和验证精度
plt.clf() # 清空图像
acc = history.history['binary_accuracy']
val_acc = history.history['val_binary_accuracy']
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
总结
- 通常需要对原始数据进行大量预处理,以便将其转换为张量输入到神经网络中。单词序列可以编码为二进制向量,但也有其他编码方式。
- 带有
relu激活的Dense层堆叠,可以解决很多种问题(包括情感分类),你可能会经常用到这种模型。 - 对于二分类问题(两个输出类别),网络的最后一层应该是只有一个单元并使用
sigmoid激活的Dense层,网络输出应该是0~1范围内的标量,表示概率值。 - 对于二分类问题的
sigmoid标量输出,你应该使用binary_crossentropy损失函数。 - 无论你的问题是什么,
rmsprop优化器通常都是足够好的选择。这一点你无须担心。 - 随着神经网络在训练数据上的表现越来越好,模型最终会过拟合,并在前所未见的数据上得到越来越差的结果。一定要一直监控模型在训练集之外的数据上的性能。